India has selected the Israeli made 3rd generation, Fire and Forget (F&F) Spike-MR anti-tank guided missile for equipping its infantry. The missile has been developed by Rafael Advanced Defense System. Rafale has tied with Kalyani Group to co-produce the missile at their joint facility at Hyderabad.
The $1 billion deal covers purchase of 321 missile launchers, 8,456 missiles and 15 training simulators. There is further option of acquiring 1,500 additional launchers, 30,000 missiles with Transfer-of-Technology (TOT). Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL), which is the main manufacturer of anti-tank missiles, will build these missiles. In fact, if news reports are to be believed, final integration of missile produced by Kalyani Rafael Advanced Systems (KRAL) will be done by Bharat Dynamics Limited.
But the above purchase decision reflects filling only one component of India's anti-tank missile requirement. A 2010 report in Times of India gives the following details of overall ATGM requirement of the army:
The Army, after all, has a shortfall of around 44,000 ATGMs of different types. "Though Army has an authorized holding of 81,206 ATGMs, not even half that number is present in its inventory,'' said a source
In this report, we take a look at India's anti-tank missile usage across multiple platforms. And how these are likely to be met in near future.
Source: internet
What is SACLOS?
With a few exceptions, bulk of anti-tank missiles are based on Semi-Automatic Command to Line of Sight (SACLOS) guidance system. SACLOS guidance has following features:
- In SACLOS, the operator has to continually point a sighting device at the target while the missile is in flight. Electronics in the sighting device and/or the missile then guide it to the target. SACLOS devices commonly work using one of these methods: wire-guided, radio-guided, or beam-riding.
- A wire-guided missile is a missile that is guided by signals sent to it via thin wires connected between the missile and its guidance mechanism, which is located somewhere near the launch site. As the missile flies, the wires are reeled out behind it command guidance.
 |
| TOW missile showing wire link between missile and launch post Source: internet |
- In case of Radio-Frequency (RF) guided missiles, the guidance is sent from the missile-post to the missile though RF mode. This is a wire-less version.
 |
| TOW-2A missile with RF guidance instead of wires |
- With beam-riding SACLOS, the sighting device emits a directional signal directed toward the target. A detector in the tail of the missile looks for the signal. Electronics in the missile then keep it centred in the beam. It differs from SARH (semi-active radar homing) and SALH (semi-active laser homing) in which the target is illuminated by a powerful emitter and a sensor in the head of missile detects the reflected emissions and directs it to the target.
Multiple Platforms, Multiple Missiles
Indian Army employs anti-tank missiles across four major platforms. These are:
- Infantry - Infantry is equipped with man-portable anti-tank guided missiles. Each infantry battalion has organic anti-tank missile platoon. The number of missile launchers/unit is higher for plains as compared to mountains.
- Mechanized Infantry - Mechanized infantry of Indian Army consists of mechanized infantry battalions under Mechanized Infantry Regiment (MIR) and The Brigade of Guards Regiment. Both of these regiments are equipped with BMP-2 Infantry Fighting Vehicles (IFV). Apart from 30mm main canon, BMP-2 also carries ATGM which is fired by the gunner of the IFV.
- Armored Corps - The T-90 tanks of the Armored Corps have the capability to fire ATGM from the main 125mm smooth-bore cannon.
- Army Aviation Corps - Till the advent of Weapon Systems Integrated (WSI) - Dhruv or Rudra attack helicopter in the army, only IAF Mi-25/35 attack helicopters carried air-to-surface anti-tank missiles. Once Light Combat Helicopter (LCH) is inducted, it will also require air-launched ATGM.
Note 1: Anti-Tank Guided Missile Battalions
Indian Army till a decade back had dedicated ATGM Battalions. From what I know, there were four such ATGM battalions, all with The Brigade of Guards. 17 Guards was one such ATGM battalion.
A 2012 report in Indian Express by noted defense analysts Mandeep Singh Bajwa, gives the following details about this battalion:
The 17 Guards, popularly known as the Tankbusters, was raised as an ATGM (anti-tank guided missile) battalion and leaders in the induction of new technology and weaponry, something which the top brass was at that time loath to initiate with regard to the Poor Bloody Infantry (PBI).
They were the first unit to be equipped with the French MILAN (Missile d´Infanterie Léger ANtichar) second-generation missile. The battalion deployed nine missile detachments during the Kargil war along with assaulting infantry battalions. These were effectively used for bunker-bursting, providing much-needed fire support capacity to the battalions they were embedded with.
The battalion now has a different role and equipment, but the same pride and professionalism which have carried it through the decades
Employment Details
Missiles operated by each of the above platforms is as under:
(A) Infantry: Milan-2/Milan-2T and Konkur-M missiles
Jeep mounted Milan-2 missile
Milan-2 is a French 2nd-generation (SACLOS - Semi-automatic command-to-line-of-sight) man-portable ATGM which is produced in India by Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL). Milan-2T is advanced version of the same missile with tandem warhead (two warheads-one behind the other).
Initially, Milan-1 was the mainstay ATGM of the infantry. Milan-2 started entering service in the IA by mid-80s and Milan-1 was phased out. Subsequently, with the proliferation of Explosive Reactive Armor (ERA) on tanks, missiles with tandem warhead became necessary.
General Staff Qualitative Requirement (GSQR) for Milan-2T was issued in 2003 and after some drama symptomatic of working of Defense Public Sector Undertakings (DPSU), order was placed for 4,100 missiles in 2008. This was to be completed in 36 months period.
However, it must be added that Milan-2T does not have a tandem warhead in true sense. Instead of two shaped charged warheads back-to-back, it has a small sharped charge at end of the probe (in addition to main sharped charge warhead) to improve armor penetration.
Evolution of Milan ATGM
(Source: internet)
(Source: internet)
(A.1) Milan/Milan-2T Usage
Milan-2/2T missiles can be mounted on a platform or operated on man-pack basis by a 2 member team consisting of a gunner and loader. The Milan-2T missile weighs 7.1 kg while the French made tripod with guidance unit weighs about 14 Kg. Total weight comes out to be 22-23 Kg. However, Indian Army uses a common missile launcher across Milan and Konkur missiles known as FLAME, which is on heavier side. More on it later.
There is no public data available on number of launchers/missiles per infantry battalion. Though, some news report spoke of each infantry battalion in the plains equipped with 4 x long range ATGM and 4 x short-range ATGM launchers. The report also speak of 1 x long range and 1 x short range ATGM launchers for battalions in mountain warfare role. This gives 8 missile launchers per battalion for plains/deserts and 2 for mountains. Number of missiles per launcher is 6 in both the cases. So, an infantry battalion in plains has 8 x 6 = 48 missiles in its inventory. The same number for mountainous region is 12 missile per battalion.
Considering 2 x missile launchers per company for a 4 x rifle company structure of Indian Army infantry battalions, 8 missiles launchers per battalion should be correct. The Konkur-M missiles are discussed in subsequent section.
Indian Army 2-man ATGM team with Milan missile and FLAME launcher
(Source: bharat-rakshak.com)
Indian Army mounted Milan missile and FLAME launcher
(Source: bharat-rakshak.com)
(A.2) FLAME launcher
If you compare the first two images above (French soldier with Milan missile and Jonga mounted Indian ATGM team) with fourth and fifth image above, you can make out the difference between the aiming and guidance kit.The first two pics show the tripod cum aiming+guidance kit as obtained from France. Fourth and fight picture show Milan missile mounted on FLAME launcher. Where FLAME stands for - Fagot Launcher Adapted to Milan Equipment.
Fagot here refers 9K111 Fagot ATGM (NATO reporting name - AT-4 Spigot) which India operated with BMP-1 vehicles. Konkur-M (NATO reporting name - AT-5b Spandrel) which is the current ATGM on BMP-2 is further development of AT-4 and utilizes a similar tripod launcher.
The FLAME launcher which has been adapted from AT-4 missile is 9P135M; this is a Soviet Union/Russian launcher which could fire both AT-4/AT-4C and AT-5 missiles.
Further, there are two versions of FLAME launcher - (a) FLAME-G: Ground version to be used only for Milan-2 missile. (b) FLAME-V: Mounted version which can fire both Milan-2 and Konkur-M/AT-5B missile and which can also be used in dismounted role. This build flexibility and mechanized troops can use Milan-2/2T if required (but not other way around)
BDL FLAME launcher for Milan missile
(Source: www.jjamwal.in)
As per BDL website, the launcher weighs 26 Kg - this is the combined weight of tripod, 9S451 guidance controller box (rectangular structure below the missile) and a9Sh119 optical sight unit. While BDL site does not mention this but the mounted version of FLAME launcher is said to be heavier at 35 kg.
For comparison purpose, check the AT-4 and AT-5 missiles with their launchers:
The blast protection sheet which gives protection to the gunner from the missile tube seems to have been carried forward from original French launcher for Milan missile.
 |
| AT-4 missile (source: internet) |
 |
| AT-5 Konkur missile (source: internet) |
(A.3) Note 2: The Kornet-E Mystery
The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) in it arms trade register documents a 2003 deal for supply of 250 launchers and 3,000 Kornet-E missiles. This has been affirmed by writing of Brigadier Gurmeet Kanwal (retd) where he mentioned induction of these missiles. It is generally believed that these missiles were imported after lesson learnt in employment of ATGMs in Kargil war. A missile like Kornet with heavy cum specialized warhead (thermobaric) will be able to take out the kind of fortified structures encountered during Kargil War.
Considering the relatively small number of launchers and missiles ordered, it is very likely that these were for specialized units like dedicated ATGM battalions (which existed earlier). But as explained in next section, ATGM units themselves have converted to tracked and wheeled Recce & Support (R&S) role.
It is not clear at present which arm - infantry or mechanized infantry - employs this potent missile.
(A.3.1) Missile details
9M113 Kornet (NATO reporting name: AT-14 ‘Spriggan’) is a heavy laser-beam riding ATGM which is meant to destroy the most well armoured tanks. It was developed as a successor to AT-4/AT-5 family of missiles with the objective of taking on the heavy western main battle tanks. But given the prize of the missile and state of Russian economy post 1991, one-on-one replacement was ruled out.
The missile has achieved fame, or notoriety, depending on who you speak to, for knocking out leading main battle tanks like US Abrams and Israeli Merkava. One of the main reasons ascribed to Hezbollah knocking out 40+ Israeli tanks during 2006 Lebanon invasion was use of Kornet-E missile.
The missile system consists of 9P163-1 portable launcher with 1P45-1 Sight Tracker, mechanical drives to steer the missile and 1PN79-1 Thermal Imager. The Kornet Missile comes in two configurations – 9M133-1 (anti-tank-HEAT-tandem warhead) and 9M133F-1 (thermobaric warhead for bunkers/fortified positions).
The missile weighs 29 kg with tube and the whole launcher with missile weights in excess of 50 Kg. The 1PN79-1 Thermal Imager itself weights more than 11 kg. Kornet-E is not exactly a man-portable system – it can be carried short-distance by a 2-man crew but needs a vehicle for longer range movement.
 |
| Kornet missile with launcher. Thermal sight 1PN79-1 can be clearly seen. (source: internet) |
It represents a very potent missile against any armor on India’s eastern or western border.
(B) Mechanized Infantry: Konkur-M missiles
Mechanized infantry, both from Mechanized Infantry Regiment (MIR) and The Brigade of Guards (or simply The Guards) have anti-tank role across two main categories:
- Mechanized Infantry Battalions: Equipped with BMP-2
- Reconnaissance & Support Battalion (Recce & Support-R&S) - R&S battalions are further of two types:
- Tracked - Equipped with BMP-2
- Wheeled - Jeep mounted ATGM and BRDM-2
(B.1) BMP-2
BMP-2 of Indian Army during R-Day Parade
(Source: www.defenceupdate.in)
Heavily camouflaged BMP-2 during exercise
(Source: bharat-rakshak.com)
BMP-2 has a single ATGM launcher mounted on the roof between the commander and gunners hatch. 9M113M 'Konkur-M' (NATO reporting name: AT-5B Spandrel B) is the standard ATGM missile. Each BMP-2 carries 4 anti-tank missiles.
The missile launcher/firing post is capable of 360 degree rotation and -5 to +15 degree elevation. Missile is fired by the gunner from within the turret without having to expose himself. This is achieved with integration of missile's optical fire-control system with the gunner's main fire-control system. Though, missile reload requires gunner/commander to expose himself. Further, each BMP-2 also carries an additional FLAME launcher to fire the missile in dismounted mode from ground and away from the vehicle.
BMP-2 firing older version of Konkur Missile (not Indian Army)
(Source: internet)
BMP-2 firing older version of Konkur Missile (not Indian Army)
(Source: internet)
(B.2) 9M113M 'Konkur-M 'Missiles
Konkur-M Missile with extended probe in front
(Source: internet)
9M113M Konkur-M missile is an evolution of 9M113 Konkur missile. Latter is referred to as AT-5 Spandrel while former is called AT-5B Spandrel.
The main difference between the two missiles is presence a probe in front of the missile and tandem High Explosive Anti-Tank (HEAT) warheads. The probe is extended from the missile on launch. The presence of probe and tandem warhead helps to defeat the Explosive Reactive Armor (ERA) on modern tank and improve armor penetration.
This video from Syria shows a Konkur-M missile being fired. As the missile is fired, the front part of the missile clears the canister and missile stop for a split second. The probe is extended and missile is ejected.
Considering that both infantry and mechanized infantry use Konkur/Konkur-M missile, it has to be the most widely held ATGM in the Indian Army.
In 2012, India entered into agreement with Russia for purchase of 10,000 Konkur-M missiles for USD 225 million. As per a report by Stockholm International Peace Research Institute`s (SIPRI) arms transfer database, Russia had supplied 7,000 missiles by 2015. Prior to this, some 28,000 Konkur and Konkur-M missiles (Konkur-M from 2003 onward) have already been manufactured/imported by BDL.
(B.3) Reconnaissance & Support Battalions (Recce & Support)
In Mid-80s, some vanilla infantry divisions were modified and termed as RAPID - Reorganized Army Plains Infantry Division. Each RAPID had 1 x Armored Brigade + 2 x Infantry Brigades. Armor Brigade consisted of 2 x Mechanized Infantry Battalions + 2 x Armored Regiments. In addition, each RAPID also had 1 x Recce & Support Battalion (some accounts say one of the two mechanized infantry battalions in armored bde was R&S battalion and there is not separate R&S battalion).There were initially four RAPID (14, 18, 24 and 36 RAPID) but the same number now stands at 6 with 4 and 12 infantry divisions having converted to RAPID. The number of Recce & Support battalions has also proliferated accordingly. And it is likely that R&S battalions have been allotted beyond RAPIDs to plain infantry divisions as well.
R&S battalions come in two variants which I think is driven by terrain and operational requirements.
(B.3.1) Reconnaissance & Support (Tracked)
These R&S battalions are equipped with BMP-2 IFV and also have Battlefield Surveillance Radar-Medium Range (BFSR-MR).In this video from "Jai Hind with Rocky & Mayur" they spend time with 17th Battalion, Brigade of Guards nicknamed as 'Tank-busters'. This is the same battalion which converted from pure ATGM role to R&S role. You can see the TATRA mounted BFSR-MR being deployed in the video.
Source: NDTV Good Times
(B.3.2) Reconnaissance & Support (Wheeled)
Wheeled R&S battalions are equipped with Jeep mounted ATGM and BRDM-2 (ATGM version - 9P148). Each BRDM-2 carries 5 x Konkur-M ready-to-fire missiles along with 10 reloads. Most likely these are also equipped with BFSR-MR.
Polish Army 9P148 BRDM-2 firing older Konkur missile
(Source: internet)
This short video shows a 9P148 BRDM-2 of Polish Army and mechanism of raising the missiles from within vehicle and swiveling them to acquire target.
You can check out this longer video of BRDM-2 of Hungarian army in action. It shows missile firing from BRDM-2 as well - https://youtu.be/G4otByrUW_s
The T-90 'Bhishma' tank of the Indian Army has the capability to fire an anti-tank missile through its main gun. This missile is called as Invar (NATO reporting name: AT-11B 'Sniper'. This is a laser beam riding, semi-automatic command-to-line of sight (SACLOS) missile. It is guided by the tank gunner through a laser guidance complex integrated with the gunner's main sight.
Details about the missile from fofanov.armor.kiev.ua:
"The 9K119M Refleks-M (AT-11 SNIPER-B) is a guided weapons system launched from the 2A46M main gun of T-80 and T-90 MBTs. The 9K119M system uses beam-riding laser guidance. The tank directs a coded beam from a special gunner's sight, which creates a laser "funnel" with the missile riding in the center. The 9K119M uses the 9M119M missile."
(C) Armored Corps: T-90 Main Battle Tank
 |
| Invar ATGM (9M-119M) |
(Source: fofanov.armor.kiev.ua)
The T-90 'Bhishma' tank of the Indian Army has the capability to fire an anti-tank missile through its main gun. This missile is called as Invar (NATO reporting name: AT-11B 'Sniper'. This is a laser beam riding, semi-automatic command-to-line of sight (SACLOS) missile. It is guided by the tank gunner through a laser guidance complex integrated with the gunner's main sight.
Details about the missile from fofanov.armor.kiev.ua:
"The 9K119M Refleks-M (AT-11 SNIPER-B) is a guided weapons system launched from the 2A46M main gun of T-80 and T-90 MBTs. The 9K119M system uses beam-riding laser guidance. The tank directs a coded beam from a special gunner's sight, which creates a laser "funnel" with the missile riding in the center. The 9K119M uses the 9M119M missile."
The ammunition round is 3UBK20 and consists of the 9M119M missile and the 9Kh949 reduced charge propellant casing with a spacer plug which seats the missile properly into the main gun.
The 3UBK20 ammunition fits into the normal autoloader on the tank, and the normal load is 6 missiles. Due to high cost of the system, usually only elite regiments shall have the missiles in a loadout.
The 9M119M missile uses a tandem configuration with the precursor charge for overcoming ERA"
Apart from seating the missile properly " the piston plus also protects the laser beam receiver at the base of the missile from propellant gasses. Since the laser beam receiver is located at the rear of the missile, it is imperative to minimize the shock of firing the missile, which is why the piston has a buffer spring" (Source:thesovietarmourblog.blogspot.in)
The image below shows the arrangement of missile (No-2) and charge-9Kh949 (No-5):
(Source: thaimilitaryandasianregion.wordpress.com)
Video of T-80 firing a Refleks missile (3UBK-14 round, 9M119 missile) of which Invar or Refleks-M is an evolution:
India signed a contract with Russia for 25,000 Invar missiles in 2011. Of these, 10,000 missiles were to come from Russia while BDL is to manufacture balance 15,000 missiles.
(D) Army Aviation Corps: Rudra & Light Combat Helicopter
Till the advent of Rudra or WSI-Dhruv, the Army Aviation Corps (AAC) did not operate any combat helicopter. In 2013, AAC accepted two Rudra helicopters and raised the 251 (Armed) Squadron. Another squadron is likely to be raised soon under Eastern Command followed by third under Northern Command.
As per media reports, IA intends to raise 06 squadrons with 10 Rudra helicopters each. Then, we have the Light Combat Helicopter (LCH) under development. It should enter service in few years and IA seems to be looking for 114 machines.
Both helicopters have capability of carrying air-launched ATGM. It was planned that HELINA (air-launched version of NAG missile) will be used for these helicopters. However, the final development phase of HELINA seems to be taking longer than expected. And IA has requested for interim purchase of foreign air-launched ATGM to fill the gap. German PARS-3 LR is a candidate for foreign acquisition. But there seems to be no movement on this purchase request at the moment.
In addition to Rudra and LCH, IA has also requested for 39 Apache attack helicopters from USA. A May 17, 2017 report in The Hindu said that IA is likely to get 11 Apaches gunships. If this induction happens, it will bring with it another type of air-launched ATGM, the famous Hellfire missile.
(E) Indigenous development
(E.1) NAG:
 |
| NAG missile |
 |
| Latest iteration of NAMICA vehicle (source: trishul-trident.blogspot.in/) |
A 2010 video of NAG missile tests. It very clearly shows the lofted profile of the missile and it hitting the top part of the tank target
- The most well-known anti-tank missile under development by DRDO. It is a 3rd Generation, Fire-and-Forget missile, top-attack missile which uses Imaging Infrared (IIR) seeker. The missile works in Lock-On-Before-Launch (LOBL) mode.
- NAG is a heavy missile weighing in excess of 40 kg and fired from a dedicated platform known as NAMICA based on BMP-2.
- It has no prior equivalence in the Indian Army and when inducted, it will represent addition of new anti-tank capability. In fact, there are only few missiles in the this class.
- The F&F guidance system means the launch vehicle can move out after firing the missile which leads to better survivability. Further, the missile is ‘top-attack’ – which means it attacks the top section of a tank’s turret, a place with weakest armour ensuring effective kill.
- As per the latest news report, the missile has successfully undergone development trials in second week of June with improved target seeker; the missile demonstrated ability to hit target at 4 km range under highest daytime temperature (11am to 3pm). It is likely that missile will now enter User-Trials.
- The Recce & Support (R&S) battalions of the army are likely to be the first candidate for these missiles.
(E.2) HELINA (Helicopter Launcher NAG):
 |
| HELINA being fired from WSI-Dhruv/Rudra helicopter (source: internet) |
 |
| HELINA missile in its launcher tube |
 | ||
Close-up of HELINA missile leaving WSI-Dhruv/Rudra. The exhausts from mid-body mounted booster rocket of the missile are visible (image source: internet)
|
- HELINA is the helicopter launched version of NAG missile.
- It is being developed for use abroad the WSI-Dhruv/Rudra and Light Combat Helicopter.
- HELINA is an advanced, third generation missile which has 7km range, Lock-on-After-Launch (LOAL) capability and 2-way RF command-and-video data link.
- The LOAL capability allows the helicopter to fire the missile in general area of the target and then use missile’s seeker to lock-on when the target becomes clear. As the missile gets closer to the target area, the missile seeker pics up the target(s). The 2-way RF command-and-video data link transfers the seeker video to gunner’s cockpit. The gunner can then place the target tracker on a specific target. Post this, the gunner can either guide the missile himself to the target or missile does so autonomously.
- The 2-way RF video-and-command link was achieved in 2011. The missile achieved 7 km range from ground-launch platform in 2013.
- In June 2014, the missile was fired from Rudra helicopter and achieved 7 km range from airborne platform.
- Again in mid-2015, ‘hot fire’ trial of HELINA was done for 7 km range. Of three missiles fired, 2 managed to hit the target.
- The missile was to be tested in September 2016 with a new Imaging Infra-Red (IIR) Seeker with more sensitive Focal Plane Array (FPA); earlier version had 128x128 FPA while September 2016 test will have missile with 640X512 FPA.
- Considering that army is keen to acquire an interim ATGM for already inducted Rudra helicopters and for those to be shortly inducted, it seems there is some development work pending on the missile
- There is unverified report that HELINA is under-going redesign to ensure the exhaust from mid-body mounted booster don't radiate outwards. Instead, the exhaust will now pass through the body of the missile and exit from the rear.
(E.3) Canon-Launched Guided Missile (CLGM)
 |
| Canon-Launched Guided Missile. Also seen is the FLAME launcher (souce: https://www.facebook.com/TejasMrca) |
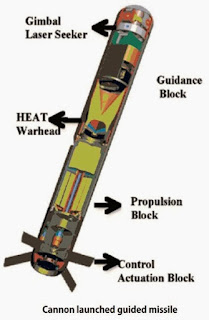 |
| Layout of CLGM (source: internet) |
 |
Source: trishul-trident.blogspot.in/
Old brochure of CLGM from 2010 when it was known as SAMHO. Notice the missile tube and missile
|
- MOD Annual Report 2014-15: Canon Launched Guided Missile (CLGM): CLGM is the semi active laser homing antitank missile which is able to engage the enemy tanks up to 5 km. The kill mechanism with CLGM is tandem high explosive anti-tank warhead. Instrumented flight trials from tripod have been successfully completed and midcourse guidance has been demonstrated.
- The missile is indigenous version of anti-tank guided missile launched from main gun of a tank. Missile caliber is 120mm and guidance is laser-beam riding SACLOS.
- In April 2017, DRDO conducted successful launch of CLGM from main gun Arjun Mk-2
- The Man-Portable ATGM (MP-ATGM) being developed by DRDO is derived from CLGM. As the above picture shows, the same is expected to fired from the FLAME launcher.
- While a lighter 14.5 kg man-portable version is being worked out, at 18.5 Kg, CLGM is only 2 kg heavier than Konkur-M (16.5 kg). May be, it can/will replace the Konkur-M as long-range ATM in use with infantry battalions.
(E.4) Amogha-1
- In early 2016, BDL tested a new missile with 2.8 km range and Radio-Frequency (RF) based guidance. There is no further news about the missile.
(E.5) RF Guidance ATGM:
- Times of India, 2nd April 2016: Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) has indigenously developed and test fired an advanced Wireless Anti-Tank Missile with RF Guidance at Babina ranges. RF System with EW protection was used to send the guidance command to the missile. The system has the capability of being remotely launched and piloted from a safe distance equaling the advantages of expensive third generation ATGMs.
- MOD Annual Report 2010-11: BDL is working on developing Radio Frequency Controlled ATGM.
- There is no further news about the missile.
(E.6) Man-Portable Anti-Tank Guided Missile (MPATGM)
 |
| Source: http://trishul-trident.blogspot.in/ |
- Ministry of Defense Annual Report 20115-16: The project was sanctioned in January 2015 towards design and development of MPATGM system comprising of 3rd generation anti-tank guided missile with launch tube, and launcher with command launch unit. During the year, design configuration has been finalized and reviewed. Eight static tests of rocket motor were conducted to achieve consistent ballistic performance. Control flight tests are scheduled in first half of 2016.
- On 29th August 2015, Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) and Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO) have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for Joint Development of 3rd Generation Man-Portable Anti – Tank Guided Missiles (MPATGM) leading to its subsequent production for the Indian Army.
- There seems to one significant difference between MP-ATGM and other laser beam riding missile like Kornet-E. Kornet-E does not rely on reflected laser for guidance. The laser it receives is gathered at the rear part of the missile. On the other hand, like smart weapons, MP-ATGM captures laser at the front section of the missile and actually rides the reflected laser beam to the target. It should also be able to hit target basis a laser designation from other source rather than the missile launcher. This gives good shoot-and-scoot opportunity to the missile fire unit.
- Development status of the missile remains unknown.
(F) Summary of Missile & Technical Data
The table below summarizes the range, weight, guidance and other dimensions of the missiles already operational, to be inducted or under R&D phase.
Conclusion
As the write-up shows, Indian Army has a varied types of anti-tank guided missiles depending upon usage and platform. In pure number terms, the total requirement is in excess of 85,000 missiles of different types.
The recent order for Spike-MR fills only one, albeit large, part of the overall requirement. If the infantry battalions indeed use a mix of short and long range ATGM, then Spike-MR represents replacement of only the short range version i.e. Milan/Milan-2T. The field is wide open for replacement of Konkur-M in long range ATGM for the infantry. CLGM mentioned above has the attributes to be this replacement. It remains to be seen whether CLGM/CLGM derived missile is the answer or we import another missile. Spike family has the Spike-LR version and Israelis will sure push it. Considering that Konkur-M are going strong, I think domestic R&D establishment still has some time on their hand to offer a credible solution for this requirement.
But induction of Spike-MR does mean that doors for US made Javelin ATGM are more or less closed. It does not make sense for an army to operate two man-portable ATGMs. It might so happen that IA may import some units for specialized formations like special forces. But even this seems absurd.
BMP-2 are slated for upgrade. One proposal from the Russians talks of re-arming the BMP-2 with four AT-14 Kornet missiles; these are placed on either side of the turret in a ready-to-fire pack of two. With DRDO making progress with CLGM, it remains to be seen if it can be adapted for BMP-2 upgrade. Between infantry's long range ATGM requirement and BMP-2 upgrade, CLGM/CLGM derived missile has the potential to tap the biggest segment of ATGM in the army.
Recently, Indian Army has expressed interest for next generation tank fired ATGM for its T-90 fleet. And it seems the T-72 main gun (2A46M) is also likely to be updated with T-90 main gun (2A46-M5). This will permit upgraded T-72 to fire ATGM from the main gun. CLGM was developed for 120mm rifled main gun of Arjun tank while T-72/T-90 have 125mm main guns. It remains to be see whether DRDO bites the bullet and delivers a new missile for T-90/T-72 fleet or India goes for missile from abroad.
Finally, NAG seems to that much closer to clearing the final hurdle. This one missile represents a phenomenal jump in anti-tank capability of the army. The missile is capable of defeating any present or future tank which is likely to see service on western or eastern borders. It induction in the army will give formidable anti-tank capability to its infantry/mechanized formations.
Same goes for HELINA. The Army Aviation Corp (AAC) is slated for massive expansion, especially in the attack helicopter domain. IA plans to induct 60 Rudra and 114 Light Combat Helicopters. It is but common sense that a domestic missile serves this massive requirement.
As things stand today, India can fulfill about 80%-85% of ATGM requirement across multiple platforms. All it requires is for the R&D establishment to work out realistic and achievable goals. And for the Indian Army to ensure good does not become the enemy of the best and that it works closely with the R&D establishment to work on this road-map.
Please share you comments, feedback and do point out mistakes.



























No comments:
Post a Comment